| Кол-во комнат | Холодный туман
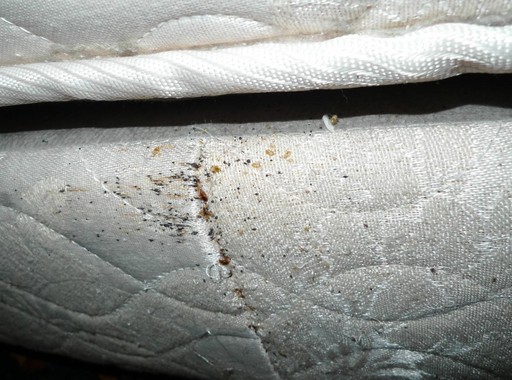
Холодный туман – технология уничтожения насекомых посредством распыления отравляющего состава комнатной температуры. Мощный парогенератор преобразует инсектицидный раствор в густой пар из микрочастиц размером до 80 микрон. В течение 3 часов инсектицид находится во взвешенном состоянии и максимально заполняет собой все пространство помещения. Постепенно оседая, инсектицидное облако укрывает собой все поверхности, в том числе стены и потолок. Частицы яда проникают в щели за мебелью, зазоры между плинтусами и стеной, в полости под отслоившимися обоями и другие труднодоступные места, где чаще всего обитают насекомые. Оптимальный вариант для квартир и небольших закрытых помещений. |
+ барьерная защита
Холодный туман
Холодный туман – технология уничтожения насекомых посредством распыления отравляющего состава комнатной температуры. Мощный парогенератор преобразует инсектицидный раствор в густой пар из микрочастиц размером до 80 микрон. В течение 3 часов инсектицид находится во взвешенном состоянии и максимально заполняет собой все пространство помещения. Постепенно оседая, инсектицидное облако укрывает собой все поверхности, в том числе стены и потолок. Частицы яда проникают в щели за мебелью, зазоры между плинтусами и стеной, в полости под отслоившимися обоями и другие труднодоступные места, где чаще всего обитают насекомые. Оптимальный вариант для квартир и небольших закрытых помещений. Барьерная защита — обработка специальным гелем для профилактики проникновения насекомых извне. |
Горячий туман
Метод обработки горячим туманом схож с холодным туманом. Принцип действия тот же – генератор тумана наполняется инсектицидным раствором, который распыляется в помещении. Но в данном случае раствор нагревается до 90°C, в результате чего он распадется на еще более маленькие частицы – размером всего до 10 микрон. Они остаются во взвешенном состоянии до 10 часов. Туман заполняет собой все щели и даже микротрещины поверхностей. Именно эта особенность на долгое время зависать в воздухе и максимально заполнять пространство и делает горячий туман самым эффективным способом уничтожения насекомых. Лучшее решение для больших площадей и помещений с высокой степенью зараженности. |
+ барьерная защита
Горячий туман
Метод обработки горячим туманом схож с холодным туманом. Принцип действия тот же – генератор тумана наполняется инсектицидным раствором, который распыляется в помещении. Но в данном случае раствор нагревается до 90°C, в результате чего он распадется на еще более маленькие частицы – размером всего до 10 микрон. Они остаются во взвешенном состоянии до 10 часов. Туман заполняет собой все щели и даже микротрещины поверхностей. Именно эта особенность на долгое время зависать в воздухе и максимально заполнять пространство и делает горячий туман самым эффективным способом уничтожения насекомых. Лучшее решение для больших площадей и помещений с высокой степенью зараженности. Барьерная защита — обработка специальным гелем для профилактики проникновения насекомых извне. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 к.кв. | 1600 руб. | 2600 руб. | 4400 руб. | 6100 руб. |
| 1 к.кв. + препараты без запаха | 3800 руб. | 4700 руб. | 6500 руб. | 7900 руб. |
| 2 к.кв. | 1900 руб. | 3000 руб. | 4600 руб. | 6500 руб. |
| 2 к.кв. + препараты без запаха | 4100 руб. | 5100 руб. | 6700 руб. | 8400 руб. |
| 3 к.кв. | 2100 руб. | 3200 руб. | 4800 руб. | 6800 руб. |
| 3 к.кв. + препараты без запаха | 4300 руб. | 5300 руб. | 6900 руб. | 8800 руб. |
| 4 к.кв. | 2300 руб. | 3400 руб. | 5000 руб. | 7100 руб. |
| 4 к.кв. + препараты без запаха | 4500 руб. | 5500 руб. | 7100 руб. | 9100 руб. |
| Кухня, санузел и коридор | 1500 руб. | 2500 руб. | 3000 руб. | 7500 руб. |
| Кухня, санузел и коридор + препараты без запаха | 3500 руб. | 4500 руб. | ||
| Гарантия | 1 год | 1 год | 1 год | 1 год |

Избавим вас от любых вредителей
Перезвоним за 30 секунд!






















 Опыт работы – 10 лет
Опыт работы – 10 лет



